Pulmonary embolism (Guidelines) | Right Decisions
1/4 – Đánh giá khả năng lâm sàng; Geneva giản lược
D-dimer hoặc D-dimer điều chỉnh theo tuổi cho người trên 50 tuổi
CTPA
PE xác nhận
PE loại trừ
PE loại trừ
Chuyển sang phần 2: Quản lý thuyên tắc phổi
Geneva giản lược
Tiền sử DVT/PE
1
Nhịp tim 75–94
1
Nhịp tim ≥95
2
Phẫu thuật hoặc gãy xương trong vòng tháng qua
1
Ho ra máu
1
Ung thư đang hoạt động
1
Đau một bên chi dưới
1
Đau khi sờ vào tĩnh mạch sâu ở chi
1
Tuổi ≥65
1
Tính D-dimer điều chỉnh theo tuổi:
- Với người trên 50 tuổi: nhân tuổi với 10.
- D-dimer chỉ dương tính ở người trên 50 tuổi nếu kết quả báo dương vượt quá mức D-dimer điều chỉnh theo tuổi.
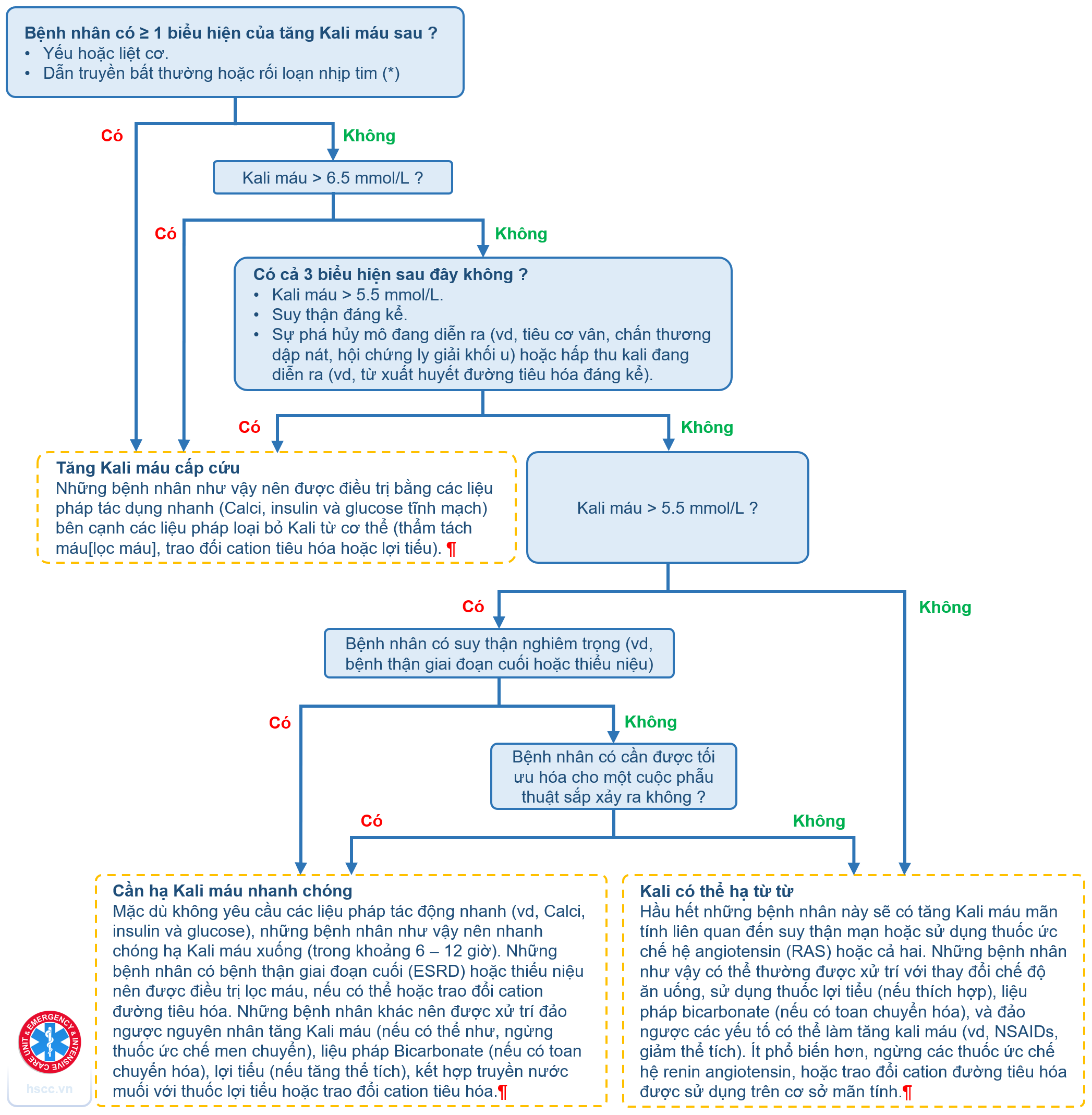
Rối loạn huyết động
Bệnh nhân có bất kỳ một trong các dấu hiệu sau hay không:
a) ngừng tim
b) sốc tắc nghẽn
HA tâm thu <90 mmHg hoặc cần vận mạch để đạt HA ≥90 mmHg dù đã bù thể tích đầy đủ VÀ thiếu máu cơ quan
c) hạ huyết áp kéo dài
HA tâm thu <90 mmHg hoặc giảm HA tâm thu ≥40 mmHg kéo dài >15 phút và không do nhịp tiết hình mới, giảm thể tích máu, hoặc nhiễm khuẩn – và thiếu máu cơ quan
Chuyển sang thrombolysis
Thảo luận với bác sĩ cấp trên
- Cân nhắc bổ sung dịch 250–500 ml
- Quá nhiều dịch trên 500 ml có thể làm trầm trọng gắng sức tâm thất phải.
Tất cả bệnh nhân có PE xác nhận đều cần:
- Đánh giá chức năng tâm thất phải (RV) từ CTPA
- Điểm s PESI đơn giản (sPESI)
Troponin
Có lý do nào khác để giữ bệnh nhân ở viện không? (ví dụ: lâm sàng, xã hội, khó tiếp cận y tế)
Nguy cơ trung bình–cao
Nhập viện nội trú, cân nhắc theo dõi tại MHDU hoặc CCU
Nguy cơ trung bình
Nhập viện nội trú
sPESI: PESI đơn giản
Tuổi >80
1
Ung thư
1
Suy tim mạn
1
HR ≥110
1
HA systolique <100
1
Độ bão hòa động mạch <90%
1
Trong trường hợp ngừng tim/ gần ngừng tim
Đánh giá chống chỉ định với thrombolysis (nếu khả thi) và thực hiện thrombolysis khi được chỉ định lâm sàng và phê duyệt bởi bác sĩ cấp trên.
Tiêm alteplase 50 mg như bolus trong 1–2 phút. Trong ngừng tim, có thể tiêm thêm 50 mg khác dưới dạng bolus; trong trường hợp gần ngừng tim không tiến triển thành ngừng tim, cho thêm 50 mg dưới dạng IV infusion trong 2 giờ.
Lưu ý: liều dùng ở ngừng tim/ gần ngừng tim là không được cấp phép.
Trong bệnh nhân mất hemodynamics (không ngừng tim/ gần ngừng tim):
Đánh giá chống chỉ định với thrombolysis và tiến hành nếu phù hợp lâm sàng và được phê duyệt bởi bác sĩ cấp cao.
Tiêm alteplase theo bảng dưới:
Trọng lượng cơ thể
- [Bảng liều cụ thể sẽ được điều chỉnh theo trọng lượng; vui lòng tham khảo hướng dẫn nội bộ hoặc của tổ chức y tế tương ứng để liều chi tiết.]
Alteplase Dose
65kg
100mg over 2 hours, administered as:
- 10mg IV bolus over 1 to 2 min
- THEN 90mg IV infusion over 2 hours
<65kg
1.5mg/kg over 2 hours, administered as:
- 10mg IV bolus over 1 to 2 min
- THEN remainder of dose as IV infusion over 2 hours
Injectable Medicines Guide access:
- IV monograph accessed via NHS Injectable Medicines Guide – Alteplase (Medusa) (NHS Highland intranet access required).
- Direct link: NHS Injectable Medicines Guide (password protected, available via Medicines Information).
- Also available via the Clinical Applications page of the NHS Highland intranet.
Absolute contra-indications to thrombolysis include:
- Intracranial neoplasm
- Recent (<2 months) intracranial or spinal surgery or trauma
- History of a haemorrhagic stroke
- Active bleeding or bleeding diathesis (eg, severe thrombocytopenia)
- Treatment with anticoagulant
- Or non-haemorrhagic stroke, within the previous three months.
Relative contra-indications to thrombolysis include:
- Severe uncontrolled hypertension (systolic blood pressure >200 mmHg or diastolic blood pressure >110 mmHg)
- Non-haemorrhagic stroke more than three months prior
- Surgery within the previous 10 days
- Pregnancy
- Haemorrhagic or ischaemic stroke in preceding 6 months
Complete drug information: Actilyse 10 mg powder and solvent for solution for injection and infusion – Summary of Product Characteristics
Following thrombolysis, patients should be stepped down to unfractionated heparin (UFH) or treatment dose low molecular weight heparin (LMWH). This decision should be based on clinical response to thrombolysis, and individual bleeding risk. UFH should only be administered in level 2 or 3 settings.
Step down to unfractionated heparin (UFH) for 24 – 48 hrs
If the patient has had LMWH within the previous 12 hours:
- DO NOT give a bolus dose, but commence UFH via continuous infusion.
- Prescribe on the “Unfractionated Heparin (UFH) Prescription Chart for Intravenous (IV) Infusion", available in critical care areas.
- Ensure UFH is also prescribed on the Kardex, “as per chart” or via the placeholder on HEPMA "HEPARIN Infusion – AS PER PAPER CHART".
- The suggested dose is 18 units/kg/hour but doses are weight banded on the prescribing chart for ease of use.
If the patient has NOT had LMWH within the previous 12 hours:
- Give a bolus dose of UFH 75 units/kg over 3 to 5 minutes. Doses are weight banded on the prescribing chart for ease of use.
- Prescribe on the “Unfractionated Heparin (UFH) Prescription Chart for Intravenous (IV) Infusion”, available in critical care areas.
- Ensure UFH is also prescribed on the Kardex, “as per chart” or via the placeholder on HEPMA "HEPARIN Infusion – AS PER PAPER CHART".
- Immediately following the bolus dose, commence UFH via continuous infusion.
Monitoring whilst on UFH
Check APTT ratio 4 hours after commencing UFH and adjust dose as per Unfractionated (UF) Heparin Prescription Chart for Intravenous (IV) Infusion.
Check APTT ratio 4 hours after any adjustment is made to the infusion rate.
Once stable, check APTT ratio 12 hourly during treatment.
- *
Step down to LMWH
Enoxaparin is the LMWH of choice in NHS Highland. The first dose of enoxaparin should be given immediately post thrombolysis, unless there are any immediate signs of bleeding. If patients were already prescribed treatment dose enoxaparin prior to thrombolysis, check dosing below, and restart LMWH.
Criteria
Enoxaparin dose
CrCl ≥ 30mL/min AND low risk of recurrence
1.5mg/kg once daily by SC injection
CrCl ≥ 30mL/min AND additional risk factors e.g. obesity, cancer, recurrent VTE, symptomatic PE
1mg/kg twice daily (12 hourly) by SC injection
CrCl < 30mL/min
1mg/kg once daily by SC injection
The maximum single dose of enoxaparin is 120mg. In patients who weigh >120kg, start with 120mg every 12 hours (provided CrCl ≥ 30mL/min), and seek specialist haematology advice +/- monitoring of factor Xa levels.
Step down to oral therapy
When stepping down from UFH to apixaban, stop the continuous infusion and give the first dose of apixaban at the same time.
When stepping down from treatment dose LMWH to apixaban, give apixaban at the next scheduled dose of LMWH. Do NOT give LMWH at the same time and ensure LMWH is discontinued on the Kardex or HEPMA.
More detailed information on anticoagulant switching is available: Anticoagulant switching | Right Decisions
For more details on apixaban prescribing, see section “Direct oral anticoagulants”
Confirmed pulmonary embolism
Refer to section 3
Refer to flowchart when haemodynamically stable.
Renal impairment (ie: creatinine clearance <15L/min
LMWH
See chart for dosing information
DOAC contraindicated or unsuitable?
DOAC
See chart for dosing information
First-line option:
Apixaban
- 10mg twice daily for 7 days, THEN
- 5mg twice daily for at least 3 months (See: Treatment duration and follow-up)
Detailed drug information, including dose adjustments for weight and renal function: Apixaban 5mg Film-Coated Tablets – Summary of Product Characteristics (SmPC)
Second-line options:
Rivaroxaban
- 15mg twice daily for 21 days, THEN
- 20mg once daily for at least 3 month (See: Treatment duration and follow-up)
- NB rivaroxaban must be taken with food
Detailed drug information, including dose adjustments for weight and renal function: Xarelto 15mg film-coated tablets – Summary of Product Characteristics (SmPC)
Dabigatran and edoxaban.
- Note: Requirement for 5 days of treatment dose LMWH before initiating dabigatran or edoxaban for PE.
- See SPC’s for detailed prescribing information.
Notes:
- All patients commenced DOAC should have their medications reviewed to check for significant drug interactions and drugs which may be associated with a cumulative bleeding risk:
- Check detailed drug interaction information at Medicines Complete — Stockley’s Interactions Checker
- Antiplatelets: consider stopping, unless clear indication to continue antiplatelet in combination with DOAC. Consider discussing with Cardiology, where appropriate. Document rationale for co-prescribing
- NSAID’s: bleeding risk, avoid where possible. If short term use required, ensure limited duration and GI protection considered
- All patients initiated on DOAC should receive verbal and written information prior to discharge, see: DOAC Counselling Tool (NHS Highland intranet access required)
DOAC contra-indicated or unsuitable at present:
Low Molecular Weight Heparin (LMWH): Enoxaparin, prescribed as per guidance above.
Treatment Duration
Provoked PEs (transient/ reversible risk factor)
- Discontinue anticoagulation after 3 months (6 months in active cancer)
Unprovoked or recurrent PEs:
- Continue anticoagulation for at least 6 months and refer to PE clinic
Follow-up
Patients who should be referred to the PE service for follow-up include:
- All patients under the age of 50 with PE
- All unprovoked PE
- Recurrent PE
- All intermediate-high and high risk PE, as determined by the Risk Stratification above
Treatment duration >6 months may be appropriate for high risk / recurrent PE patients. Final decision will be made at PE clinic.
The investigation and management of PE in pregnancy falls outwith this guidance and therefore should NOT be used.
Please contact Obstetrics / Gynaecology urgently if a pregnant patient presents with suspected or confirmed PE.